Enzyme Lab Report
Biology William Mahnke, Adison Akery, Chase Lyles, Ben Buran
Peroxidase Enzyme Activity
Peroxidase Enzyme Lab
Question
How does the level of pH in a solution affect the rates of enzymatic reactions (chemical reactions that are assisted by enzymes)?
Background
Enzymes act as catalysts and speed up chemical reactions by lowering the energy needed for a reaction to begin otherwise known as activation energy. Substrate in the case of enzymes is the material that “binds” with the enzyme to form a product. Substrate will often take different paths in order to create the product. During these varying paths, there a transitional or intermediate product that is formed between the final product and the reactants or beginning products. And usually the energy that is needed to start a reaction is the same as the energy needed to create this intermediate product. One of enzymes’ numerous jobs is to make it easier for the substrate to become the intermediate state. So that means that the reaction doesn’t need as much energy as before because the transitional state is easier to reach. Enzymes are large protein molecules that are folded together to create a binding site for substrate also known as the active site. The bindings will transform a substrate into its transitional state. Sometimes, enzymes will change the shape of their bindings to match the shape of the substrate. Depending on the organ an enzyme is in, certain conditions will make the enzyme either perform better or sometimes worse enough the active site of the enzyme. When this happens, an enzyme or many enzymes become denatured. The conditions that can affect how productive an enzyme can be are the temperature, the level pH, the concentration of substrate and the concentration of enzymes. The main enzyme for this lab is peroxidase. The optimum conditions for this enzyme are a temperature or 10-70 degrees celsius and a pH level of 4-11. These conditions can vary depending on where the peroxidase enzyme is located, in a certain organ.
Materials
- Tap water
- Handsoap
- Buffer solution with pH of 9.00
- Safety goggles
- Glass beakers
- Grass
- Mortar and pestle
Procedure
- Put on safety goggles.
- Get the water, buffer solution of 9.00 pH, and hydrogen peroxide
- Put the grass in the mortar and pestle and beat it until it is liquid
- Pour liquid grass into a beaker
- Pour water into the beaker with the liquid grass
- Repeat steps 4 and 5 for hand soap and hydrogen peroxide
- Measure the enzymatic reactions for each liquid by the amount of oxygen or the thickness of the layer of foam in the beaker.
Results
For the results, we first had to choose how to measure the effects of the different solutions. The two ways we could’ve measured the results. The first idea would be to measure how much would be transformed into water. This idea came into a problem that it would be difficult to measure the amount of water created. First, our control for the experiment was water so it would be hard to differ the original water and the water after the enzymic reaction. Second, we were mixing each solution will liquid grass and the color of the liquid could make it hard to distinguish the liquid grass from the water. So, our other option was to measure how many molecules were transformed into oxygen. As really are only other option, we went with that measurement. As the results showed, the hydrogen peroxide performed the best by far. For each of the solutions, we did two tests and would average the two results to get our data. The hydrogen peroxide had a layer of bubbles that was 1.3cm thick on average, the water was .3cm thick, and the buffer solution of pH 9.00 had bubbles that was .8cm thick.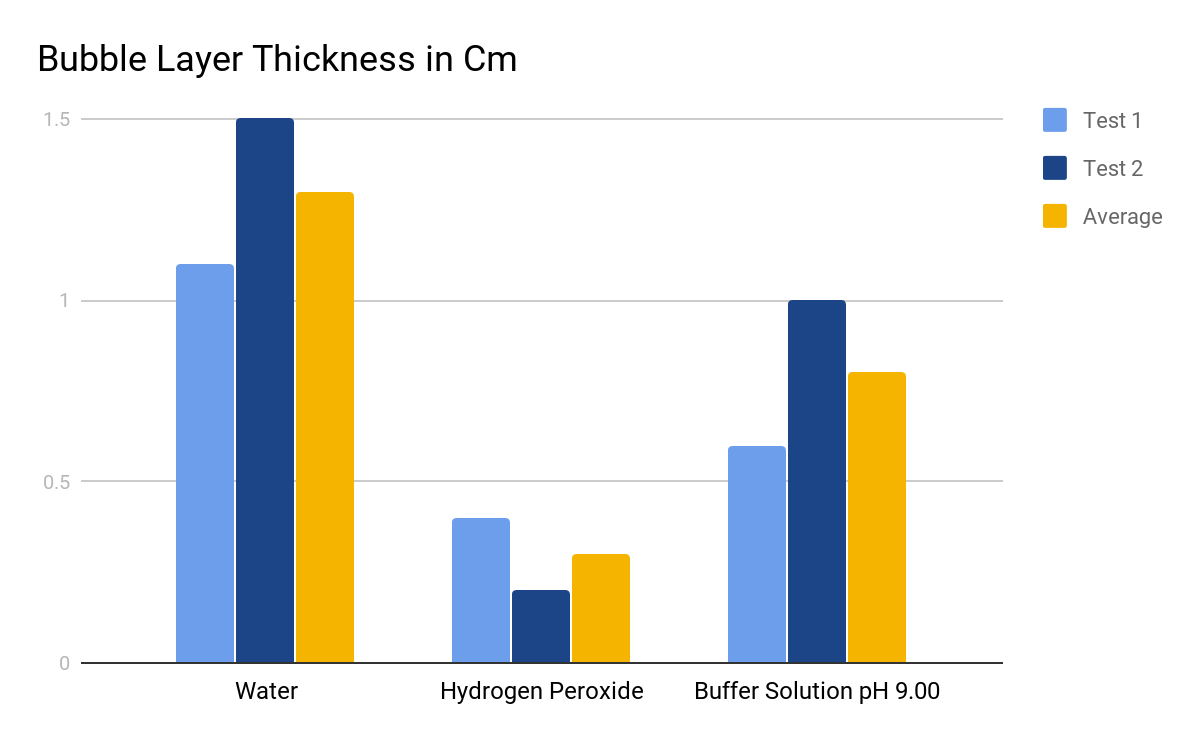
Conclusion
In summary, hydrogen peroxide had the most enzymic reactions overall when mixed with the liquid grass. It clearly outperformed water and the buffer solution and would be the most ideal case for enzymes in that scenario. Our group decided that there were two key parts of the experiment that we could’ve worked on. The first idea we had post experiment was that we could’ve added another solution to test to better answer our question. If we were to repeat this experiment, adding another liquid, could’ve gave us a better solution for the question we were trying to solve. The second thought we had was to had done for tests for each of the solutions. More solutions means for data which means the evidence is more reliable. So if this experiment was repeated, it would’ve been better to have three, possibly four tests per item tested. When we looked at our results, we began to understand why we got the results. We realized how the molecules in the hydrogen peroxide affected the outcome. Hydrogen peroxide has two oxygen molecules and two hydrogen molecules. This abundance of oxygen means that oxygen was a product of the reactions.

Comments
Post a Comment